dbt-core1.11.2
Published
With dbt, data analysts and engineers can build analytics the way engineers build applications.
pip install dbt-core
Package Downloads
Authors
Project URLs
Requires Python
>=3.10
Dependencies
- agate
<1.10,>=1.7.0 - click
<9.0,>=8.2.0 - daff
>=1.3.46 - dbt-adapters
<2.0,>=1.15.5 - dbt-common
<2.0,>=1.37.2 - dbt-extractor
<=0.6,>=0.5.0 - dbt-protos
<2.0,>=1.0.405 - dbt-semantic-interfaces
<0.10,>=0.9.0 - jinja2
<4,>=3.1.3 - jsonschema
<5.0,>=4.19.1 - mashumaro
[msgpack]<3.15,>=3.9 - networkx
<4.0,>=2.3 - packaging
>20.9 - pathspec
<0.13,>=0.9 - protobuf
<7.0,>=6.0 - pydantic
<3 - pytz
>=2015.7 - pyyaml
>=6.0 - requests
<3.0.0 - snowplow-tracker
<2.0,>=1.0.2 - sqlparse
<0.5.5,>=0.5.0 - typing-extensions
>=4.4
dbt enables data analysts and engineers to transform their data using the same practices that software engineers use to build applications.
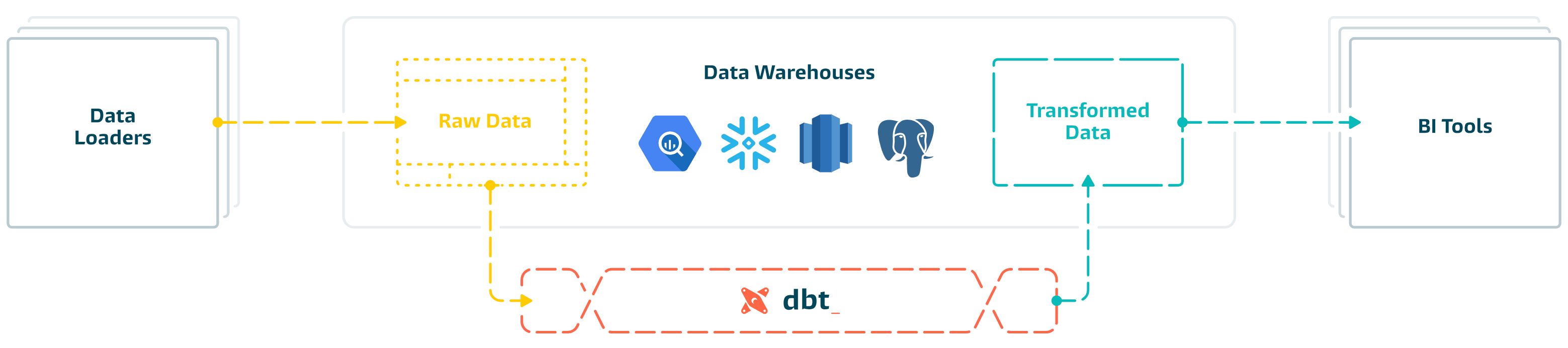
Understanding dbt
Analysts using dbt can transform their data by simply writing select statements, while dbt handles turning these statements into tables and views in a data warehouse.
These select statements, or "models", form a dbt project. Models frequently build on top of one another – dbt makes it easy to manage relationships between models, and visualize these relationships, as well as assure the quality of your transformations through testing.
Getting started
- Install dbt
- Read the introduction and viewpoint
Join the dbt Community
- Be part of the conversation in the dbt Community Slack
- Read more on the dbt Community Discourse
Reporting bugs and contributing code
- Want to report a bug or request a feature? Let us know on Slack, or open an issue
- Want to help us build dbt? Check out the Contributing Guide
Code of Conduct
Everyone interacting in the dbt project's codebases, issue trackers, chat rooms, and mailing lists is expected to follow the dbt Code of Conduct.